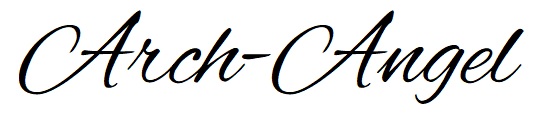Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetic foot problems are complications that can arise from diabetes. Diabetics often experience reduced blood flow and nerve damage, making them more susceptible to injuries that may go unnoticed. By prioritizing foot care, diabetics can significantly enhance their quality of life and reduce the risk of severe complications. If you have diabetes, adopting these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing serious foot problems. If you notice any changes or issues with your feet, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Here are the causes and prevention methods for diabetic foot problems.
Causes:
1. Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar levels can damage nerves in the feet, leading to a loss of sensation. This makes it difficult for individuals to feel injuries or pressure.
2. Poor Circulation: Diabetes can lead to reduced blood flow to the feet, making it harder for wounds to heal and increasing the risk of infections.
3. Foot Deformities: Conditions like Charcot foot (a condition where the bones in the foot weaken and collapse) can alter foot structure and increase the risk of injury.
4. Infections: Minor cuts or blisters can become infected due to impaired immune response and poor blood flow.
5. Dry Skin: Diabetes can cause dry skin, leading to cracks and fissures that can become entry points for bacteria.
Prevention:
1. Regular Foot Inspections: Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling. Early detection is crucial for preventing complications.
2. Maintain Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels within target ranges can help prevent nerve damage and circulation issues.
3. Wear Proper Footwear: Choose well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning, avoiding tight or narrow shoes that may cause pressure points.
4. Practice Good Foot Hygiene: Wash your feet daily with mild soap and water, and dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
5. Moisturize: Apply lotion to prevent dry skin, but avoid putting lotion between the toes to reduce the risk of fungal infections.
6. Seek Professional Help: Regular check-ups with a podiatrist can help monitor foot health and address any issues early.


Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot and connects the heel bone to the toes. Early intervention, including proper stretching, footwear choices, and personalized treatment plans, can significantly alleviate symptoms and enhance mobility. Here are the causes and prevention methods for plantar fasciitis:
Causes:
1. Overuse: Repetitive activities such as running, walking, or standing for long periods can strain the plantar fascia.
2. Foot Structure: Flat feet, high arches, or an abnormal walking pattern can put additional stress on the plantar fascia.
3. Obesity; Excess body weight can increase pressure on the plantar fascia, making it more susceptible to injury.
4. Improper Footwear: Shoes that lack proper arch support or cushioning can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis.
5. Age: The condition is more common in middle-aged individuals, as the plantar fascia can become less flexible with age.
Prevention:
1. Wear Supportive Shoes: Choose shoes with good arch support and cushioning to help reduce stress on the plantar fascia.
2. Avoid High-Impact Activities: If you're prone to plantar fasciitis, consider low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to reduce strain on your feet.
3. Stretch and Strengthen: Regularly stretching the calf muscles and plantar fascia can help maintain flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of injury.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight can alleviate excess pressure on the feet.
5. Gradual Increases in Activity: When starting a new exercise program, gradually increase intensity and duration to avoid overloading the plantar fascia.
Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails occur when the edge of a toenail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain, redness, and swelling. Regularly monitoring your toenails and seeking professional advice at the first sign of discomfort can help prevent further issues. Proper nail trimming techniques, wearing well-fitting shoes, and maintaining good foot hygiene are essential steps in managing and preventing ingrown toenails. Here are the causes and prevention methods for ingrown toenails:
Causes:
1. Improper Nail Trimming: Cutting toenails too short or rounding the edges can lead to ingrowth.
2. Tight Footwear: Shoes that are too tight or narrow can put pressure on the toes, encouraging the nail to grow into the skin.
3. Foot Injuries: Trauma to the toe, such as stubbing or repeated pressure from activities like running, can cause the nail to become ingrown.
4. Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing ingrown toenails due to the shape of their nails.
5. Poor Foot Hygiene: Inadequate foot care can lead to infections or inflammation around the nail, increasing the risk of ingrowth.
Prevention:
1. Proper Nail Trimming: Cut toenails straight across and avoid rounding the edges to prevent them from growing into the skin.
2. Choose Well-Fitting Shoes: Wear shoes that provide enough room for the toes, avoiding tight or narrow footwear.
3. Maintain Foot Hygiene: Keep feet clean and dry, and moisturise the skin around the nails to prevent dryness and cracking.
4. Be Cautious with Activities: Protect your feet during activities that may lead to toe injuries, such as wearing protective footwear during sports.
5. Address Foot Issues: If you have foot deformities or other conditions that may contribute to ingrown toenails, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management.
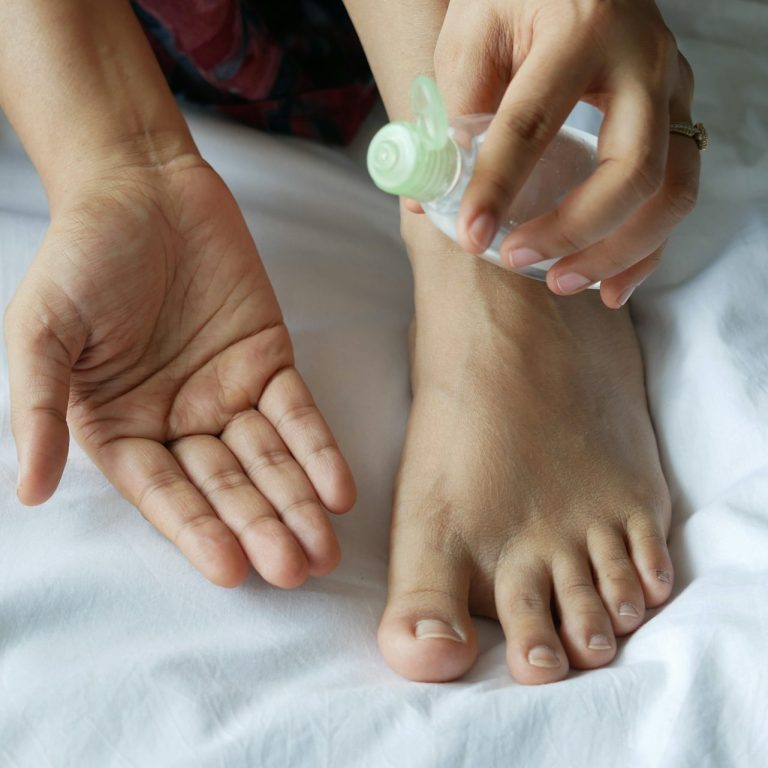
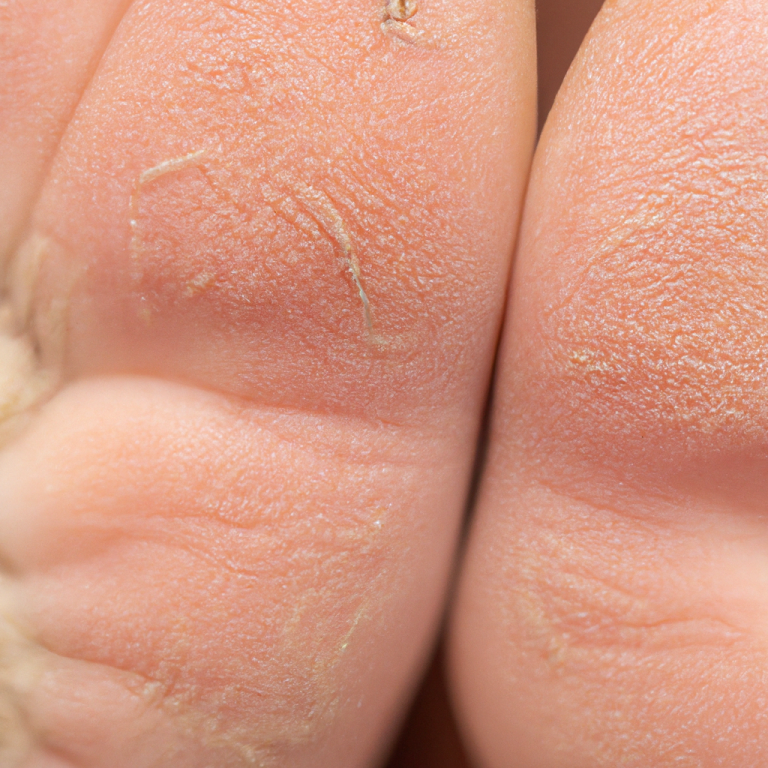
Corns and Calluses
As a foot care specialist, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of regularly managing corns and calluses. Corns and calluses are thickened areas of skin that develop in response to pressure or friction. Regularly inspecting your feet and seeking professional care can help prevent these issues, ensuring your feet remain healthy and pain-free. Here are the causes and preventions for both:
Causes:
1. Friction and Pressure Repeated friction from shoes, tools, or other surfaces can lead to the formation of corns and calluses.
2. Foot Deformities Conditions like bunions or hammertoes can create uneven pressure on the feet.
3. Improper Footwear: Shoes that are too tight, too loose, or lack proper support can contribute to the development of these skin issues.
4. Activities: Certain activities, such as running or playing sports, can increase friction on specific areas of the feet or hands.
5. Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions can make the skin more prone to thickening.
Preventions:
1. Proper Footwear: Wearing well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support can minimize friction and pressure.
2. Foot Care: Regularly moisturizing the feet can help keep the skin soft and reduce the risk of corns and calluses.
3. Padding: Using protective pads or insoles can help cushion areas that experience frequent pressure.
4. Avoiding Repetitive Stress: If participating in activities that cause friction, take breaks and alternate with different activities.
5. Foot Hygiene: Keeping your feet clean and dry can prevent skin conditions that may lead to corns and calluses.
Verrucas
Verrucas, commonly known as plantar warts, are benign growths on the soles of the feet caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These can spread easily though skin contact and touching infected surfaces. Regular monitoring and timely intervention can prevent the verruca from spreading and developing into a more significant issue. Remember, early action is key to preventing complications and promoting foot health. Here are the causes and prevention methods for verrucas:
Causes:
1. HPV Infection: Verrucas are caused by a viral infection from specific strains of HPV that enter the skin through small cuts or breaks.
2. Foot Trauma: Any injury or irritation to the skin on the feet can increase the risk of developing warts.
3. Warm, Moist Environments: Areas like swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers provide ideal conditions for the virus to thrive and spread.
4. Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems may be more susceptible to HPV infections and the formation of warts.
5. Direct Contact: Touching a wart on someone else’s foot or sharing personal items, such as towels or shoes, can facilitate the spread of the virus.
Prevention:
1. Practice Good Foot Hygiene: Keep your feet clean and dry, and regularly inspect them for any signs of warts or skin changes.
2. Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Areas: Wear flip-flops or water shoes in communal showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms to minimize exposure to the virus.
3. Do Not Share Personal Items: Avoid sharing towels, shoes, or socks with others to reduce the risk of transmission.
4. Protect Any Injured Skin: Cover any cuts or abrasions on your feet with a bandage to prevent HPV entry.
5. Boost Immune Health: Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can support your immune system, making it less susceptible to infections.

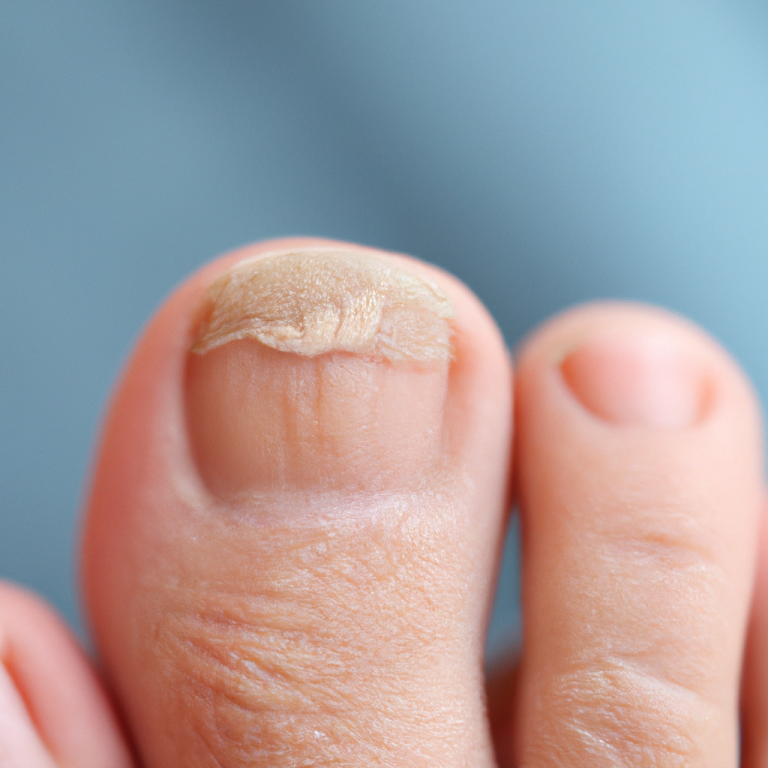
Fungal Nail Infection
Fungal toenail infections, also known as onychomycosis, occur when fungi invade the nail bed and nail plate. This can be a persistent and uncomfortable issue, particularly for those seeking the expertise of a foot care specialist. A foot care specialist can provide targeted treatments and advice on proper foot hygiene. Here are the causes and prevention methods for fungal toenail infections:
Causes:
1. Fungal Exposure: Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments. Walking barefoot in public places like swimming pools, showers, or locker rooms can expose feet to fungi.
2. Poor Foot Hygiene: Infrequent washing and drying of feet can create an environment conducive to fungal growth.
3. Nail Trauma: Damage to the nail or surrounding skin can allow fungi to enter and cause an infection.
4. Pre-existing Conditions Individuals with diabetes, weakened immune systems, or circulatory issues are at higher risk of developing fungal infections.
5. Tight Footwear Wearing shoes that do not allow proper ventilation can create a damp environment for fungi to thrive.
Preventions:
1. Practice Good Hygiene: Regularly wash and dry your feet thoroughly, paying special attention to the areas between the toes.
2. Choose Breathable Footwear: Wear shoes made from breathable materials and avoid tight-fitting shoes that can trap moisture.
3. Use Antifungal Powder: Applying antifungal powder or spray to your feet and inside shoes can help reduce moisture and fungal growth.
4. Avoid Barefoot in Public Areas Wear flip-flops or water shoes in public showers, pools, and locker rooms to minimize exposure to fungi.
5. Trim Nails Properly: Keep toenails trimmed and filed to reduce the risk of injury and make it less likely for fungi to enter.